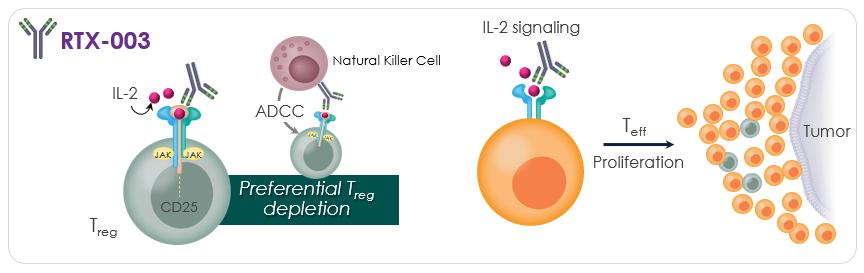
RTX-003 stimulates anti-tumor immunity by depleting immunosuppressive Treg cells via engagement with Natural Killer [NK] Cells
Discovery Oncology
iBio has three oncology products in the discovery stage. All three products are antibodies that should benefit from iBio’s Glycoengineering Technology which enables afucosylation of the molecule to enhance antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (“ADCC”). Greater ADCC conveys greater potency for cancer cell killing effects. We expect the oncology pipeline to continue to grow via the Collaboration and Option Agreement with RubrYc, as well as the Company’s partnership with an antibody discovery firm Fair Journey (see Strategic Alliances, Collaborations, and Joint Ventures below for additional details).
Vaccines:
Human Health: SARS-CoV-2
Coronavirus disease 2019 (“COVID-19” or “COVID”) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, Hubei, China, and has resulted in an ongoing pandemic. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath or breathing difficulties, and loss of smell and taste. While most people have mild symptoms, some people develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), possibly precipitated by cytokine dysregulation, multi-organ failure, septic shock, and blood clots.
The biopharmaceutical industry successfully and rapidly rose to the challenges of the COVID pandemic, delivering highly effective vaccines in record time. However, by the summer of 2021, many experts concluded that the COVID crisis is likely to be endemic to many regions around the world given the rapid emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants requiring ongoing management and responsiveness. As a result, numerous unmet vaccination needs remain:
| ◾ | Capability and capacity to address spike protein variants like Delta, for years to come |
| ◾ | Greater durability via generation of memory T cells |
| ◾ | Removing global barriers to access, including the high costs of many of the first-generation vaccines and cold-chain logistical challenges |
| ◾ | “Fear of the needle” and other patient hesitancy |
We initiated preclinical work on vaccine designs that might overcome some of the challenges associated with the first-generation vaccines that target only the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. In particular, we seek to design and
3
